
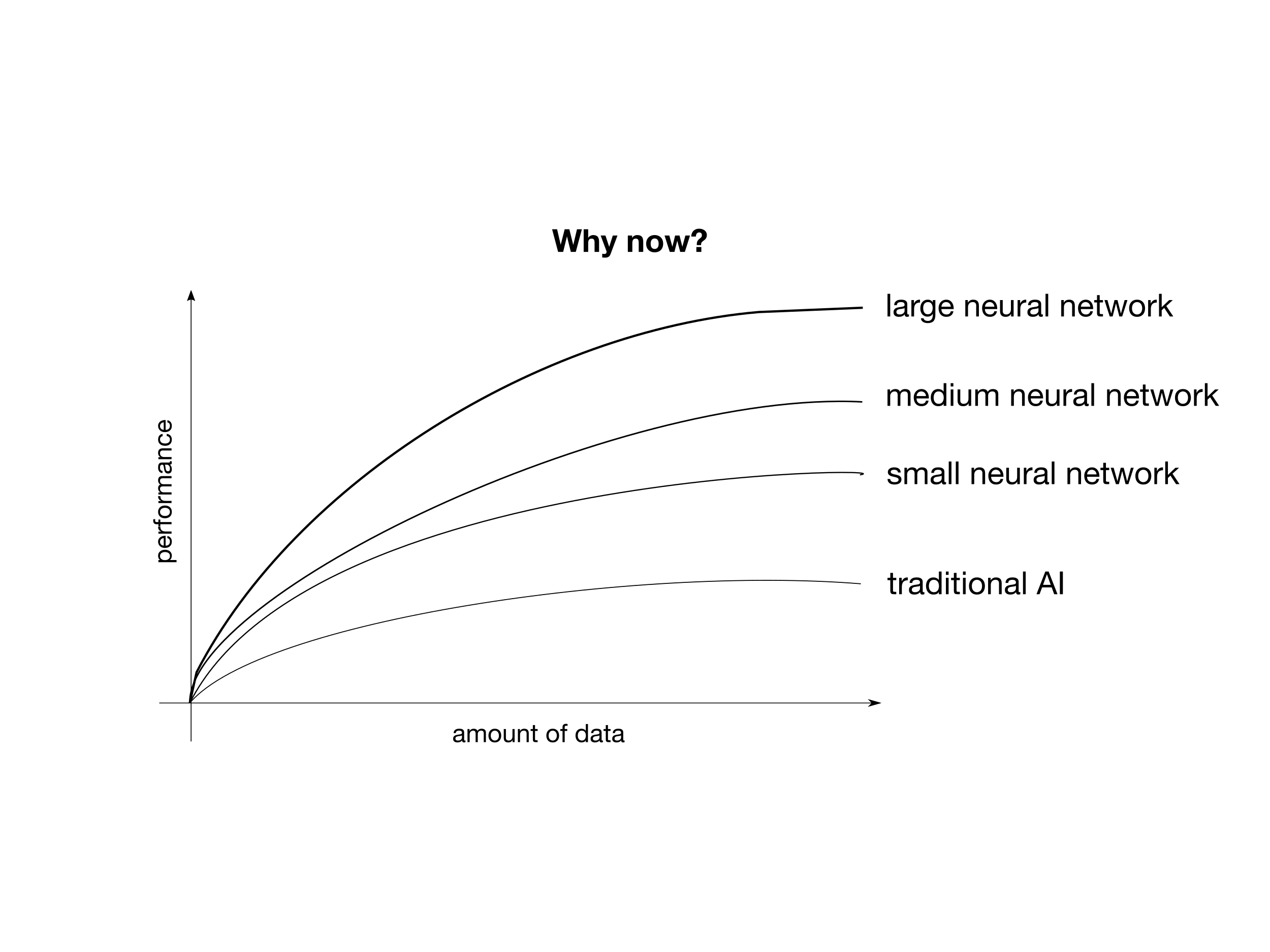
Computer Neural Network have their origins in algorithms that tried to mimic the brain and were used for the first time in the 1980's and early 1990's and had a resurgence around 2005 and were introduced as 'Deep Learning'. Now, machine learning uses neural networks in everything from climate change to online advertising, based on a simplified mathematical model of a neuron.
"An Artificial neural networks (ANNs), also shortened to neural networks (NNs) is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely model the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection, like the synapses in a biological brain, can transmit a signal to other neurons. An artificial neuron receives signals then processes them and can signal neurons connected to it. The "signal" at a connection is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. The connections are called edges. Neurons and edges typically have a weight that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Neurons may have a threshold such that a signal is sent only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold.
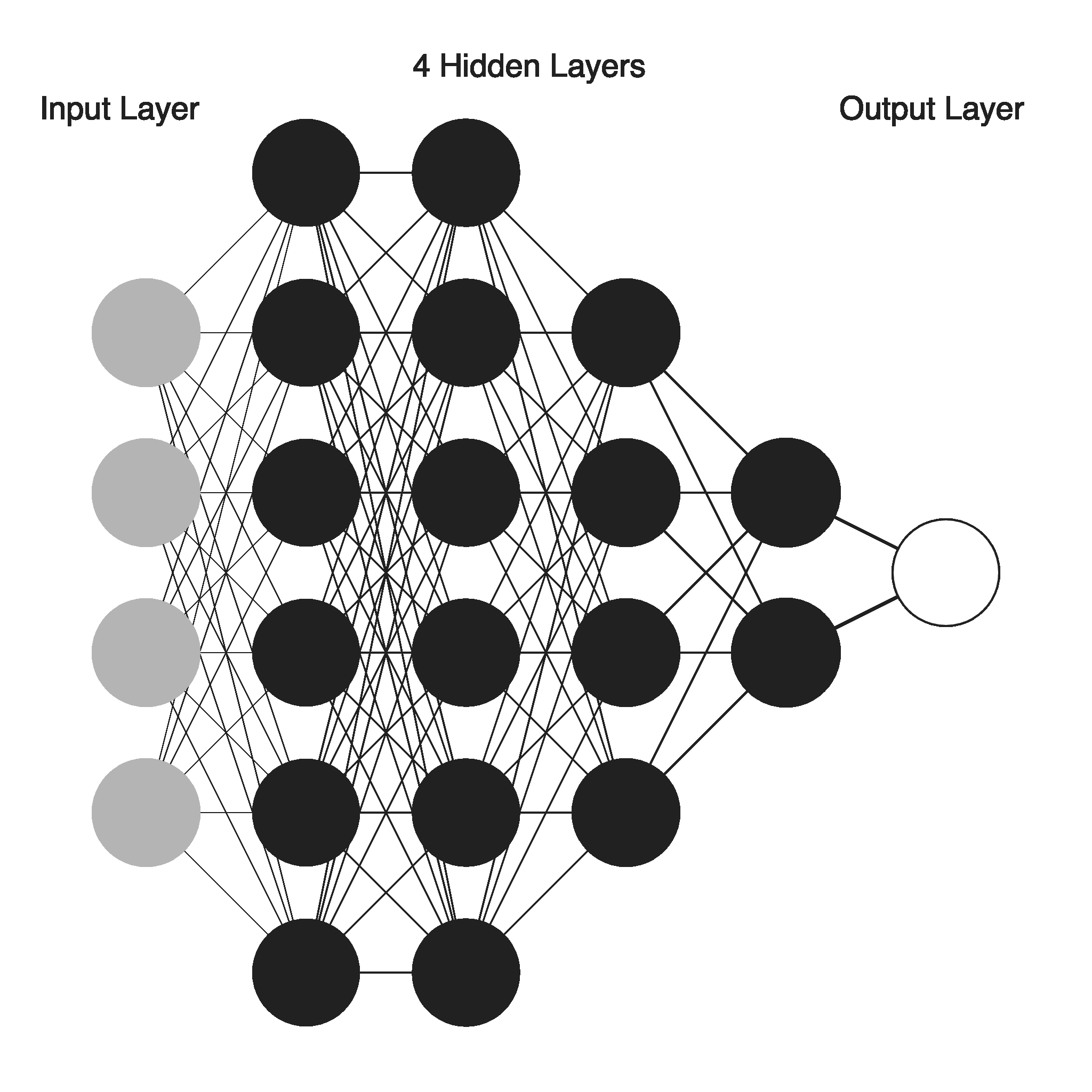
Typically, neurons are aggregated into layers. Different layers may perform different transformations on their inputs. Signals travel from the first layer (the input layer), to the last layer (the output layer), possibly after traversing the layers multiple times.
A network is typically called a deep neural network if it has at least 2 hidden layers."[1]
[1] Read more at Wikipedia.